Are you thinking of becoming a government teacher in Rajasthan, India?
In this article, I have summarized the different types of teachers, their required qualifications, age criteria, salary expectations, selection processes, and potential for career progression. It covers both government and private teaching roles, as well as opportunities in central government schools.
Key Takeaways
- Comprehensive overview of the teaching profession in Rajasthan.
- The government teaching system, with clear qualifications, selection processes, and promotion paths.
- The variability in the private teaching sector, particularly in terms of salary and selection methods.
- The role of a teacher in shaping students’ lives suggests a societal value placed on education.
Key Facts and Theme
- Types of Government Teachers in Rajasthan: There are three primary categories of teachers in the Rajasthan context:
- First Grade Teachers (PGT – Post Graduate Teachers): Teach classes 11th and 12th.
- Second Grade Teachers (TGT – Trained Graduate Teachers): Teach classes 9th to 10th.
- Third Grade Teachers (Primary Teachers): Divided into Level 1 (classes 1st-5th) and Level 2 (classes 6th-8th).
- The Role of a Teacher: Beyond imparting subject knowledge, teachers are portrayed as having a broader role in shaping students’ moral, social, and personal development. They “provide inspiring assistance to students.”
- Qualifications & Age Requirements: Each teacher type has specific educational qualifications and age requirements.
- Selection Processes: These are based on examination and document verification processes for each type of teaching role.
- Salary & Career Progression: Starting salaries and avenues for promotion are discussed for both government and private sector teachers.
- Central Government Schools: Central government schools such as Kendriya Vidyalaya, Navodaya Vidyalaya, and Sainik Schools.
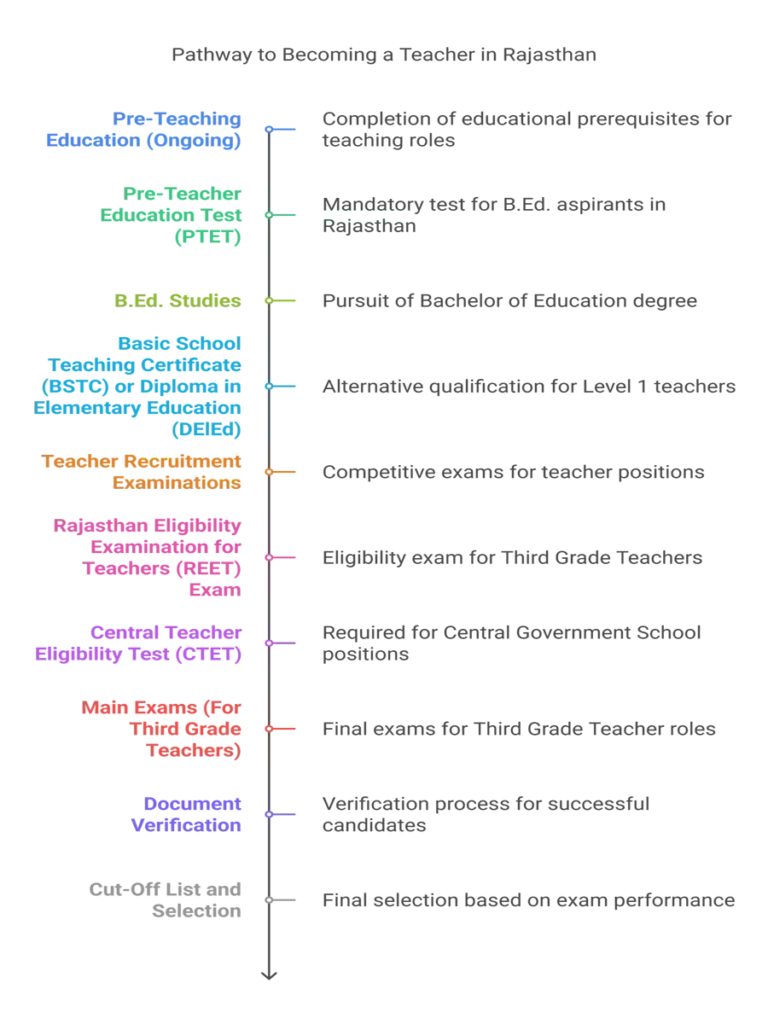
Teacher Types and Qualifications
First Grade (PGT): Classes Taught: 11th & 12th
- Qualifications: “At least a post-graduation degree” in any stream (MA, MCom, MSc, etc.), plus a B.Ed. degree. “In Rajasthan to turn into a teacher you should do a B.Ed.” Requires passing the Pre-Teacher Education Test (PTET) to pursue B.Ed.
- Age: Required – Minimum 21 years, and maximum 40 years.
- Selection Process: Exam conducted by RPSC (Rajasthan Public Service Commission), two papers: General Knowledge and subject-specific exam. Followed by document verification and a merit-based cut-off list.
Second Grade (TGT): Classes Taught: 9th to 10th
- Qualifications: Graduation in any stream (BA, BSc, BCom etc.), plus a B.Ed. degree.
- Age: Required – Minimum 18 years, and maximum 40 years.
- Selection Process: Exam conducted by RPSC, two papers: General Knowledge and subject-specific exam. Followed by document verification and a merit-based cut-off list.
Third Grade (Primary):
Level 1 (Classes 1st-5th):
- Qualifications: 12th pass plus either Basic School Teaching Certificate (BSTC) or Diploma in Elementary Education (D.El.Ed).
Level 2 (Classes 6th-8th):
- Qualifications: Graduation plus a B.Ed. degree.
- Age: Required – Minimum 18 years, and maximum 40 years.
- Selection Process: Requires clearing the REET (Rajasthan Eligibility Examination for Teachers) exam, followed by a main exam, document verification, and a merit-based cut-off list. “The REET exam is basically an eligibility exam, until your REET exam is cleared, you will not be able to give the main exam.”
Private School Teachers:
- Qualifications: Minimum graduation plus a B.Ed degree.
- Age: Required – Minimum 18 years, maximum age varies by school.
- Salary: Starting from 15,000 to 20,000 rupees, increases with experience.
- Selection Process: Varies by school, may involve interviews, tests, or both. “There is no fixed selection process.”
Central Government School Teachers (Kendriya Vidyalaya, Navodaya Vidyalaya, Sainik Schools):
- Qualifications: Minimum graduation plus a B.Ed degree.
- Age: Required – Minimum 18 years, and maximum 40 years.
- Salary: Starting salary from 35,000 to 1,00,000 rupees, varies with the level of teaching.
- Selection Process: Must clear the Central Teacher Eligibility Test (CTET) then apply for vacancies.
Salaries and Career Progression
Government Teacher Salaries (Approximate):
- First Grade (PGT): Starting salary of 60,000 rupees after probation period, with yearly increases.
- Second/Third Grade: Starting salary of 40,000-50,000 rupees, with yearly increases.
Private Teacher Salaries: Starting from 15,000-20,000 rupees, increasing with experience.
Central Government School Teacher Salaries: Starting salary 35,000 to 1,00,000 depending on the level of teaching and experience.
Promotion in the Government Sector:
- Third-grade teachers can be promoted to Headmasters of primary schools.
- Second Grade teachers can be promoted to Vice Principal or Principal with 5-10 years of experience.
- First Grade teachers can be promoted to Principal and further to District Education Officer (DEO). “The key job role of a DEO is to deal with all of the government schools in that district or city.”
- DEOs can be further promoted to Director of Education.
- Promotion through departmental exams is also possible: “If you want to get promoted faster, you can apply for government vacancies and clear the exams to get promoted.”
Conclusion
Becoming a teacher in Rajasthan involves a clear path of education, qualifications, and examinations. The specific requirements vary depending on the grade level, the type of school (government, private, or central government), and the desired career trajectory. The Bachelor of Education (B.Ed) degree is important for many roles and the need to pass specific entrance or eligibility tests for government positions. Teachers are not just instructors but guides for moral and social development.
Frequently Asked Questions: Becoming a Government Teacher in Rajasthan
There are three main types of teachers in Rajasthan: First Grade Teachers (also known as Post Graduate Teachers or PGTs) who teach students in classes 11th and 12th; Second Grade Teachers (also known as Trained Graduate Teachers or TGTs) who teach students in classes 9th to 10th; and Primary Teachers (also known as Third Grade Teachers) who teach students in classes 1st to 5th. Third grade teachers can be further categorized into Level 1 teachers (classes 1st-5th) and Level 2 teachers (classes 6th-8th).
To become a First Grade Teacher, you need a post-graduate degree (MA, MCom, MSc, etc.) in any stream, along with a Bachelor of Education (B.Ed) degree. In Rajasthan, a Pre Teacher Education Test (PTET) is required to qualify for B.Ed studies. The minimum age requirement is 21, and the maximum is 40.
For a Second Grade Teacher role, a minimum of a Bachelor's degree in any stream (BA, BSc, BCom, etc.) is required, along with a B.Ed degree. The age requirement is between 18 and 40 years old.
For a Level 1 Third Grade Teacher, you need to have completed 12th grade plus either a Basic School Teaching Certificate (BSTC) or a Diploma in Elementary Education (D.El.Ed). For a Level 2 Third Grade Teacher, you need a Bachelor's degree in any stream plus a B.Ed degree. The age requirement is between 18 and 40 years old for both levels.
The selection process generally involves an examination conducted by the Rajasthan Public Service Commission (RPSC) for First and Second Grade Teachers. This usually includes two papers: one on General Knowledge and the other on the subject the teacher wants to teach. For Third Grade teachers, the selection process includes passing the REET exam first, followed by a main exam. All successful candidates will have to undergo document verification and be included in a cut-off list for final selection.
A minimum requirement to become a private school teacher is a Bachelor’s degree in any stream along with a B.Ed degree. The minimum age is 18, but there is no fixed maximum age as it varies between schools. The selection process also varies between schools, with some using only an interview and others using both an interview and a subject-specific test. Salary usually starts from around 15,000 - 20,000, but can increase with experience.
To apply to Central Government schools, you must have a minimum of a Bachelor's degree in any stream and a B.Ed degree. The age requirements are between 18 and 40. The selection process begins by passing the Central Teacher Eligibility Test (CTET). After passing, candidates can apply for vacancies when they are advertised on the official Central Government website. Salary can start from around 35,000 to 100,000 depending on the age group taught.
Third Grade Teachers with some years of experience may be promoted to Headmaster of a primary school. Second Grade Teachers may be promoted to Vice-Principal (or Principal with a very strong track record) after 5-10 years. First Grade Teachers may be promoted to Principal after 5-10 years, and potentially to District Education Officer (DEO) with more experience and a good track record. A DEO manages all government schools in the city, and promotions are possible beyond this role to Director of Education. Teachers can also apply for higher-grade teacher positions in government vacancies and pass an exam to promote themselves faster.
Glossary of Key Terms
- First Grade Teacher (PGT): Also known as Post Graduate Teacher, they teach students in classes 11th and 12th.
- Second Grade Teacher (TGT): Also known as Trained Graduate Teacher, they teach students in classes 6th to 10th.
- Primary Teacher (Third Grade Teacher): Teachers who educate students in classes 1st to 5th; they are also divided into Level 1 (classes 1-5) and Level 2 (classes 6-8).
- B.Ed: Bachelor of Education degree, a professional qualification for teaching.
- BSTC: Basic School Teaching Certificate; a qualification for teaching primary classes in Rajasthan.
- D.El.Ed: Diploma in Elementary Education; an alternative qualification for teaching primary classes in Rajasthan.
- PTET: Pre Teacher Education Test; a required exam in Rajasthan to qualify for B.Ed studies.
- RPSC: Rajasthan Public Service Commission; the body that conducts exams for First and Second Grade teachers in the government sector.
- REET: Rajasthan Eligibility Examination for Teachers; the eligibility exam to become a third grade teacher in Rajasthan.
- CTET: Central Teacher Eligibility Test; the eligibility exam to become a teacher in Central Government schools.
- Headmaster: A teacher, promoted to the management role of a primary school.
- Principal: The head of a secondary or higher secondary school.
- Vice-Principal: An administrator below the principal in a school.
- District Education Officer (DEO): A district-level official responsible for managing all government schools in the city.
- Director of Education: The highest administrative role in the education system.




